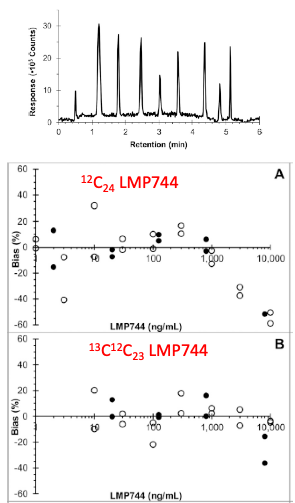
Generic assay platform with a choice of potential Internal standards, and use of Isotopologues to extend the dynamic range of the assay. Parise, RA, et al. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021; 203: 114185. PMCID: PMC8783698.Examples of Assays
Selected Projects
The CPPF has developed, validated and implemented assays for (but not limited to): abiraterone, alisertib, ATRA, belinostat, berzosertib, bortezomib, busulfan, cabozantinib, celecoxib, ceralasertib, cetuximab, copper, cyclophosphamide, dasatinib, docetaxel, elimusertib, enzalutamide, erlotinib, etoposide, fluorouracil, gemcitabine, hydroxychloroquine, imatinib, indenoisoquinoline 400, 776, 744, iohexol, irinotecan, iso-fludelone, ixabepilone, lapatinib, neratinib, nilotinib, paclitaxel, palbociclib, peposertib, phenyl-isothiocyanate, platinating agents carboplatin, cisplatin and oxaliplatin, sulforaphane, temozolomide, tetrahydrouridine, topotecan, triapine, veliparib, vincristine, vorinostat. This list is always being expanded and does not include the many compounds generated by medicinal chemists that have been subjected to animal pharmacokinetic and metabolic studies supported by the CPPF. These assays have primarily involved LC-MS or LC-MS/MS instrumentation, and have been applied to in vitro, animal and human PK studies performed at Hillman or elsewhere. We also perform select small molecular biomarker assays and ELISA based protein analyses.
For example, we developed a generic high-performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry approach for quantitation of small molecule compounds without availability of isotopically labelled standard, with an 8 min run time. Performance of the generic approach was evaluated with seven drugs. The generic approach has become a useful tool to further define the pharmacology of drugs studied in our facility.
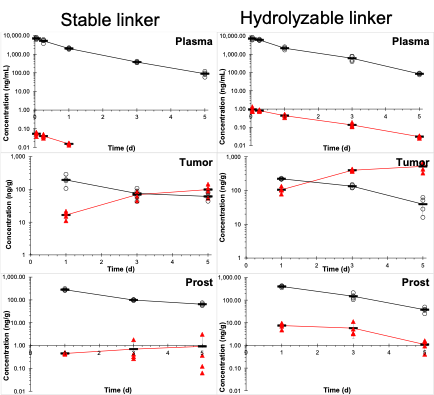
Concentrations of PSMA targeted parent drug (O) and MMAE payload (Δ) in plasma, tumor, and normal prostate after 0.8 mg/kg IV dosing to mice. Olatunji, FP, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022; 21(11): 1701-1709. PMCID: PMC9842478.
Preclinical Studies
The CPPF has been critical to the successful competition for and completion of a variety of Hillman program projects funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Among the most prominent of these are contract 75N91021D00019 (NCI) "Preclinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacology Evaluations of Agents Being Developed for Cancer Patients." which is one of three such contracts funded by the NCI nationally to develop information in support of molecules proposed for subsequent clinical trials.
The CPPF has also provided important support to a variety of grant funded projects including R21 CA223121 (NCI) "PSMA - targeted small-molecule drug conjugates." Our work verified the In vivo behavior of PSMA targeted conjugates of MMAE In plasma and relevant tissues, and explained the better antitumor activity of the analogues with more hydrolyzable linkers. PK calculations suggested ~36% of the MMAE was released by the hydrolyable linker as opposed to only 1% of the more stable linker. High MMAE In tumor and low MMAE In plasma and normal prostate confirmed the presence of a therapeutic window.
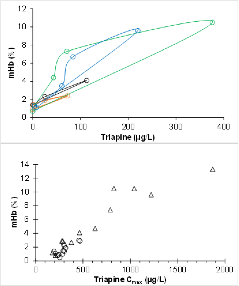
Triapine plasma concentrations correlate with percentage methemoglobine In cancer patients.
Clinical Studies
The CPPF is home to one of only 2 PK consortia U24 CA247643 (NCI) "PITT-CAL ETCTN PK Resource Laboratory" which serves the NCI Experimental Therapeutics Clinical Trial Network, compromised of most large NCI-designated Cancer Centers. Clinical samples from across the nation come to our facility for bioanalysis and subsequent Integration of pharmacological and clinical Insights gained during conduct of these early trials.
Biomarkers of Drug Effect
Pharmacodynamic biomarkers have long been studied in our facility. One of the recent examples is the study of dUrd incorporation into DNA as a function of ATR inhibition. This misincorporation was shown to be rescuable by thymidine supplementation, and was associated with IFN signaling.
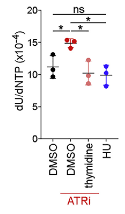
Quantitation of dU contamination in genomic DNA from CD8+ T cells. Sugitani N, et al. Cell Rep. 2022 ;40(12): 111371. PMCID: PMC9646445.
External Collaboration
The Hillman CPPF serves numerous other medical institutions and pharmaceutical companies. Academic partners include Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Institute, Johns Hopkins, City of Hope, and Washington University. Industrial partners include Novartis, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Infinity, Millenium, and Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, among others. Pharmacological and mass balance studies are a particular expertise.


